

Top Open Source SIEM Tools in 2025

Dmytro
May 18, 2025
5 min
Top Open Source SIEM Tools in 2025
In today's complex digital landscape, security threats are increasingly sophisticated. Organizations need robust Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions to detect, analyze, and respond to incidents effectively. While commercial platforms like Splunk or LogRhythm offer comprehensive features, their costs can be prohibitive, especially for small to medium-sized organizations.
Open source SIEM tools provide a compelling alternative. By 2025, these solutions have matured significantly, delivering powerful capabilities without the high price tag. This post explores the top open source SIEM tools available this year.
What Makes a Good SIEM Solution?
A comprehensive SIEM solution should include:
- Log Collection: Gathering logs from diverse sources
- Data Normalization: Standardizing log formats for analysis
- Correlation: Identifying patterns across events
- Alerting: Notifying teams of suspicious activities
- Visualization: Providing dashboards for insights and reporting
- Threat Intelligence: Incorporating up-to-date threat data
- Compliance Support: Enabling regulatory reporting and controls
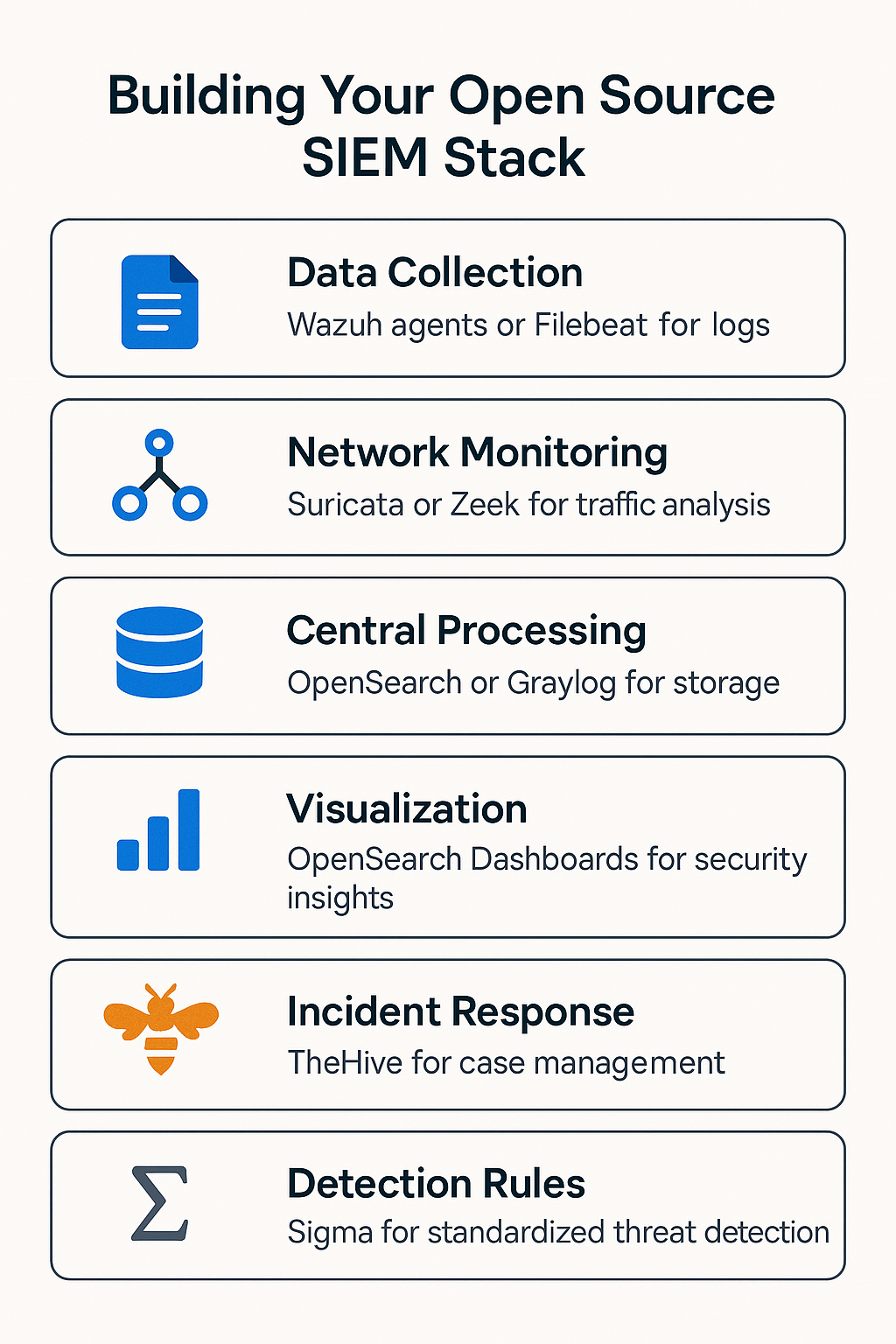
No single open source tool offers all these features out of the box, so organizations often combine multiple tools to build a complete SIEM stack.
Top Open Source SIEM Tools in 2025
Wazuh is a leading open source security platform in 2025, evolving from its OSSEC roots into a comprehensive monitoring solution.
✨ Key Features:
- Host-based intrusion detection (HIDS)
- Log data analysis and file integrity monitoring
- Vulnerability detection and configuration assessment
- Cloud security monitoring (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Compliance monitoring (PCI DSS, GDPR, HIPAA)
- Active response for automated threat mitigation
- Integration with OpenSearch for visualization
📌 Wazuh’s unified XDR and SIEM framework offers deep cloud integration and enhanced threat intelligence, providing visibility across hybrid environments—a critical need as hybrid setups dominate.
OpenSearch, a fork of Elasticsearch and Kibana, is a cornerstone of many SIEM implementations, backed by Amazon’s ongoing development.
✨ Key Features:
- Powerful search and analytics engine
- Advanced visualization capabilities
- Scalable architecture for large datasets
- Anomaly detection and machine learning
- Alerting and notification systems
- Security analytics support
📌 OpenSearch has evolved with SIEM-specific analytics and improved machine learning for anomaly detection. Community-driven security dashboards enhance its utility for security operations.
Security Onion remains a popular all-in-one Linux distribution, integrating multiple tools for unified security monitoring.
✨ Key Features:
- Network security monitoring
- Intrusion detection (Suricata, Zeek)
- HIDS via Wazuh integration
- Log management with OpenSearch
- Full packet capture
- Traffic analysis tools
- Web-based analysis interface
📌 Containerized components improve scalability and performance, while enhanced machine learning and cloud collectors keep it relevant for modern threats.
TheHive is a robust open source incident response platform, complemented by Cortex for automation, fitting seamlessly into SIEM ecosystems. Together, they streamline incident management and response.
✨ Key Features:
- Case management for incidents
- Integration with security tools
- Collaborative investigation features
- Automated responses via Cortex
- Customizable dashboards
- API-first design
📌 TheHive orchestrates incident response workflows, while Cortex automates observable analysis (e.g., checking IPs against threat feeds) and response actions like blocking threats. Their tight integration allows security teams to analyze indicators within TheHive cases and act swiftly, reducing manual effort. Expanded integrations with threat intelligence and mature automation workflows enable faster, more effective incident responses.
Graylog is a powerful log management platform with robust SIEM capabilities.
✨ Key Features:
- Scalable log collection
- Advanced search functionality
- Alerting and dashboards
- Role-based access control
- Compliance support
- Stream processing
Why It’s Great in 2025: Enhanced correlation and threat intelligence integration, paired with a refined UI, make Graylog versatile for organizations of all sizes.
Sigma_HQ isn’t a SIEM tool but a vital detection component for SIEM systems, providing standardized threat detection rules through the Sigma_HQ ecosystem.
✨ Key Features:
- Generic signature format
- Extensive threat detection rule database
- Conversion for various SIEM platforms
- Community-driven rule repository
- Tool integration
📌 Sigma Rules, stored and managed via the Sigma_HQ GitHub repository, offer portable detection logic for threats like malware or logon anomalies. Sigma_HQ’s tools convert these rules into SIEM-specific queries, ensuring compatibility across platforms like Elastic or Splunk. With thousands of rules and improved integrations, Sigma simplifies threat detection across diverse SIEM solutions.
Malcolm, a newer player, has gained traction as a network-focused SIEM tool.
✨ Key Features:
- Network traffic analysis
- Integration (Zeek, Suricata)
- Full packet capture
- Automated alerts
- Threat hunting
- Visualization and reporting
📌 Its container-based design and enhanced analytics make it a scalable, user-friendly option for network security monitoring.
Challenges of Open Source SIEM Implementation
Open source SIEMs offer cost benefits but pose challenges:
- Integration Complexity: Requires technical expertise
- Maintenance Overhead: More effort than commercial options
- Limited Support: Relies on community assistance
- Performance Tuning: Needs manual optimization
- Feature Gaps: May lack some advanced commercial features
The Future
Trends shaping 2025 and beyond include:
- AI/ML Integration: Better anomaly detection and automation
- Cloud-Native Architectures: Support for containers and serverless
- XDR Capabilities: Broader detection and response
- Threat Intelligence: Deeper integration
- Compliance Automation: Enhanced regulatory support
Conclusion
Open source SIEM tools offer viable alternatives to commercial solutions. Combining these tools creates a powerful, cost-effective security infrastructure. Organizations should assess their needs and capabilities, considering a hybrid approach with commercial tools for optimal balance.